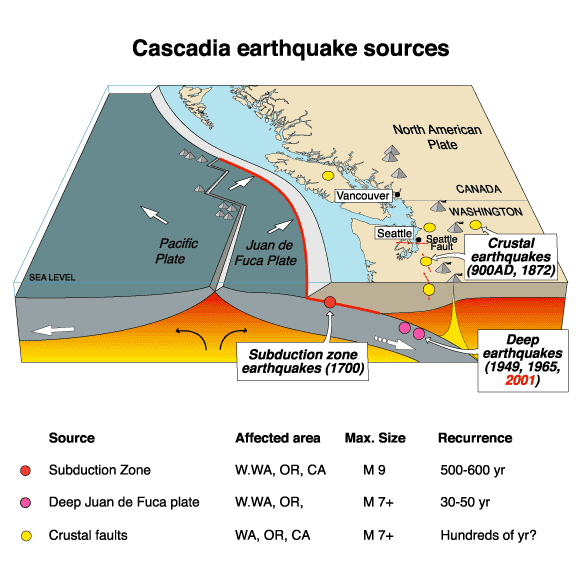
Looking at the geology of where Vancouver
is and what lies near and beneath its surface, one can understand why Vancouver
is at such high risk for earthquakes. There are plates subducting below the
less dense, North American plate which is descending below the continental
plate at a rate of 45 mm/year. Subduction occurs along the Cascadia subduction
zone. This is the second largest tectonically active fault system in North
America. The subduction zone has ruptured several times over history, causing
great earthquakes. Much of the force that leads the oceanic plates to subduct
beneath the North American plate is generated by a ridge system. The largest
ridge in Vancouver is the Juan de Fuca ridge. Grinding of the plates as it
moves along the aforementioned faults generates stress. Plate interaction along
any of the convergent, divergent, or transform faults may cause the buildup of
stress which will lead to an earthquake. With the evidence of past earthquakes
we know a major one will occur in the area along the Cascadia subduction zone
at any time. The geological setting makes this densely populated region
susceptible to frequent seismic activity.
Vancouver has an increased risk of disastrous megathrust earthquakes, the
region is surrounded by the Coast Mountains and the Pacific Ocean making it
isolated and vulnerable during a large earthquake.
Liquefaction : Is a phenomenon in
which the strength and stiffness of soil is reduced by earthquake shaking. This
is a hazard because when it occurs, the strength of the soil decreases and the
ability of soil deposit to support foundations for buildings and bridges is
reduced. It can be responsible for a tremendous amount of damage and a hazard
for many lives.
Landslides : Is the movement of rock,
debris or earth down a slope. They result from the failure of the materials
which make up the hill slope and are driven by the force of gravity. Sudden and
rapid events are most dangerous because
of the lack of warning and the speed at which material can travel down the
slope, also the force on the resulting impact. Extremely slow landslides may not
be a threat to people but it can cause considerable damage to property. There
are many resources that could be ruined, for example water supplies, fisheries,
and roads. Landslides can cause massive destruction which will impact the
economy as for all of the repair.
Tsunami : Are giant waves caused by
earthquakes or volcanic eruptions under the sea. A the waves travel inland,
they build up to higher and higher heights as he depth of the ocean decreases.
The speed of tsunmai waves depends on ocean depth rather than distance from the
source of the wave. In some cases they can result in floods reaching up to 100
feet in height. They can cause a lot of property damage, environmental damage
and leaving many lives at risk.
Flooding : Is a natural event where an
area that is dry land, suddenly gets submerged under water, Floods that happen
in areas where people live in, the water carries along the objects such as
houses, bridges, cars, furniture, and even people. It can wipe away farms and
trees as well.
Social Impact : Earthquake hazards
pose serious intermediate term risk to health and safety and economic
viability. They demonstrate risks to industrial societies from the event,
affecting everything from massive loss of life, infrastructure damage and financial
instability. Earthquakes can have short term and long term impacts. Short terms
would include people being injured, destroyed homes, disruption to
transportation and communication. Long term impacts would include a disease
being spread and peopling having to re-house.
Economic Impact : Earthquakes can
result in massive destruction of roads, bridges, farms, houses, automobiles and
people become homeless. The government deploys fireman, police and other
emergency apparatuses to help the affected. Everything comes at a heavy cost to
the people and the government. It takes years for affected communities to be
re-built and businesses to come back to normal.
Infrastructure Impacts : Earthquakes
can effect availability of many services and elements of infrastructure. The
large and violent movement of the ground caused by an earthquake will disrupt
many services. Electric line poles are vulnerable to damage. No electricity
results in no light, heat and no water. Land-line phones will not have service
as the towers may be damaged. Natural gas pipelines could also be broken.
Almost all stores rely on supplies being brought by trucks, so supply lines
will be impacted. Local airports and train facilities can also be damaged.
Bridges, buildings, and hospitals can be destroyed or damaged causing a great
effect.
Preparedness: Communities in Metro Vancouver are
preparing for the impending earthquake by making a significant investment to
assess earthquake risk, upgrade infrastructure and develop emergency plans. The
city has developed the Earthquake Preparedness Strategy to reduce the impact of
an earthquake in Vancouver. The strategies fall under four categories;
earthquake risk assessment, earthquake risk reduction, earthquake preparedness
and earthquake response and recovery. Families have made small changes in there
homes for their safety as well. For example storing food and water, having an
identified family meeting location, have an emergency prepared plan and kit,
buying self powered radios and flashlights, hanging pictures and home decor
away from where people may sit, and by simply placing heavy objects on lower
shelves.